

Identify the causes and consequences of oversecretion and undersecretion of glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and adrenal androgens. Identify the major mineralocorticoids, their biologic actions, and their target organs or tissues.ĭescribe the regulation of mineralocorticoid secretion and relate this to the regulation of sodium and potassium excretion. Understand the cellular mechanism of action of adrenal cortical hormones and identify their major physiologic actions, particularly during injury and stress. See also an introduction to the endocrine system and information about aspects of it such the locations of and hormones secreted by the main endocrine glands and conditions that affect the endocrine system including diabetes.Identify the functional anatomy and zones of the adrenal glands and the principal hormones secreted from each zone.ĭescribe and contrast the regulation of synthesis and release of the adrenal steroid hormones (glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and androgens) and the consequences of abnormalities in their biosynthetic pathways.
Increase in rate and depth of breathing.Increased blood flow through the coronary arteries and slowing of heart rate.Constriction of small blood vessels leading to increase in blood pressure.Blood supply to the bladder and intestines.Force of muscular contraction improves.Prepares the body for 'fright, fight or flight' ('FFF') and has many effects: Zones of steroid-synthesizing cells called the:Īlthough the boundaries between these zones are indistinct, each of these zones has a characteristic arrangement of cells. The adrenal cortex consists of three concentric The adrenal gland collects into large medullary veins to exit These synthesize and secrete catecholamines. The medulla consists of many large columnar cellsĬalled chromaffin cells. Hence they may be described as "richly vascularized". Both of these tissues contain many blood vessels, The most obvious aspect of the structure of the For further information about this see: (Norman Endocrine Surgery Clinic).

in the cases of certain types of tumours), one or more of the adrenal glands may be surgically removed.

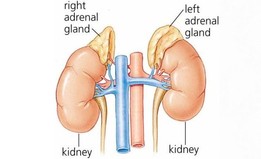
To the kidneys, and are encased in a connective tissueīuried in an island of fat. The human body normally* includes two adrenal glands.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
